Very well written post.
http://cutroni.com/blog/2014/02/05/understanding-digital-analytics-data/
2015년 12월 12일 토요일
2015년 12월 10일 목요일
GA: custom dimensions, custom metrics, custom variables
- Before: Custom Variables -> After: Custom Dimensions & Custom Metrics
- Custom Dimensions: String
- Custom Metrics: Integer
Reference:
- How to Access Custom Dimensions in Google Analytics: http://www.lunametrics.com/blog/2013/09/10/access-custom-dimensions-google-analytics/
- Implementing Custom Variables, comparing ga.js and analytics.js: http://misterphilip.com/universal-analytics/migration/variables
2015년 12월 8일 화요일
2015년 11월 23일 월요일
2015년 11월 9일 월요일
Convolutional Neural Networks
Convolutional Neural Network = Convolution + Neural Network
It is basically a neural network, but with a convolution layer.
Simply put, feeding the neural network with preprocessed features not the raw image itself.
Convolution layers do this preprocessing.
Useful Resources:
Deepcumen: http://deepcumen.com/2015/04/convolutional-neural-network/#comment-458
CS231N.Stanford: http://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/
It is basically a neural network, but with a convolution layer.
Simply put, feeding the neural network with preprocessed features not the raw image itself.
Convolution layers do this preprocessing.
Useful Resources:
Deepcumen: http://deepcumen.com/2015/04/convolutional-neural-network/#comment-458
CS231N.Stanford: http://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/
2015년 11월 7일 토요일
Statistical Inference
Statistical inference is about validating how good an estimate is.
There are two basic methods.
1. Hypothesis Testing Using Confidence intervals
- Test if null hypo falls within confidence interval
2. Hypothesis Testing Using P-values
- Test if p value is greater than alpha
Although they sound quite different, they are actually very similar, or even essentially the same.
Testing if an estimate falls within 0.95 confidence interval or if its p value is greater than alpha value of 0.05 is essentially the same logic.
There are two basic methods.
1. Hypothesis Testing Using Confidence intervals
- Test if null hypo falls within confidence interval
2. Hypothesis Testing Using P-values
- Test if p value is greater than alpha
Although they sound quite different, they are actually very similar, or even essentially the same.
Testing if an estimate falls within 0.95 confidence interval or if its p value is greater than alpha value of 0.05 is essentially the same logic.
2015년 10월 14일 수요일
Poisson Distribution as a Special Case of Binomial Distribution
I wondered that what's the difference between Poisson and Binomial Distributions.
Here's the difference, a very slight difference.
and actually, Poisson is a special case of Binomial distribution!
Poisson Distribution
Here's the difference, a very slight difference.
and actually, Poisson is a special case of Binomial distribution!
Poisson Distribution
- n (the number of trials): huge
- p (the probability of success): small
Check out this article for mathematical proof!
- Oxford Math Center: http://www.oxfordmathcenter.com/drupal7/node/297
QQ plot
- QQ plot = Normal Probability Plot = Quantile-Quantile Plot
- Tests for normal distribution
- Caution: Quantiles are points, not intervals.
- Suppose there are n samples.
- Calculate n+1-quantiles given normal distribution. (Here, the number of n+1-quantiles is n. The quantiles can be calculated with NORMSINV function in excel. Therefore, the quantiles are expressed in z scores.)
- If i-th sample's z score is smaller than i-th quantile, it will be situated below the straight line. If larger, above the straight line. This is the way how to interpret the QQ plot.
- If all sample values are above the straight line, it implies right skewness. For more examples, refer to this great question and answer from CrossValidated. (http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/101274/how-to-interpret-a-qq-plot)
2015년 10월 10일 토요일
Three matchings to be considered when preprocessing data
Three matchings to be considered when preprocessing data
1. Propensity Score between Treated and Untreated Samples
- Propensity Score Matching- Make observation resemble experiment
#If all confounding variables are identified and included as input variables along with treatment variables, is there no need to do propensity score matching?
#Even if propensity score matching helps measuring unexaggerated effect of treatment variables on target variables, would't it undermine predictive power? Say, there is a model (treatment: male/female, target: promotion) to predict whether a person would be promoted or not based on gender. Although the gender itself doesn't affect getting promoted or not, it still is a good predictor of promotion (not as a cause but as a correlation) since there are other confounding variables such as social prejudice, education, confidence, and so on.
#Machine Learning: On Correlation, Statistics: On Causation, ... something to ponder upon.
2. Ratio between Target Labels
- Data Balancing- Each label is equally distributed (1:1, 1:1:1, 1:1:1:1, etc.)
- This is not the only solution to data imbalance(skewed data). I prefer manipulating threshold in order not to lose data through down sampling.
3. Distribution of Target Labels between Train and Test sets
- (Is there a specific name assigned to this?)- Yet to explain.
#Should they match?
#Should they match even if the data is collected by experiment?
#Should test set match real world distribution? (In credit scoring, although there is a tiny amount of defaults, in model development, there should be equal amount of default as non-defaults, though not always the case.)
OpenIntro Statistics Chapter #1
OpenIntro Statistics Chapter #1
Statistics is a study of collecting and analyzing data.
Before data science, there already existed Statistics, science of collecting and analyzing data.
So, what is the difference?
Maybe where it is applied is different.
It never have been applied to business world, to be more specific, startup field, where people like to coin fancy new words.
By the way, one thing intrigued me in this chapter was a data collection part.
I never knew that regression can only be applied to data collected by random experiment.
Since my first step to data science was through machine learning, or computer science, my statistical background was bare. I applied regression to any data, whether it was collected by experiment or observations.
Therefore, in order to use regression for data collected from observations, we need to make it more alike those collected by experiment. Propensity score matching is what transforms data collected from observations to data collected from experiment, by making variables affecting the selection of treatment variable similar among treated and untreated sample.
Statistics is a study of collecting and analyzing data.
Before data science, there already existed Statistics, science of collecting and analyzing data.
So, what is the difference?
Maybe where it is applied is different.
It never have been applied to business world, to be more specific, startup field, where people like to coin fancy new words.
By the way, one thing intrigued me in this chapter was a data collection part.
I never knew that regression can only be applied to data collected by random experiment.
Since my first step to data science was through machine learning, or computer science, my statistical background was bare. I applied regression to any data, whether it was collected by experiment or observations.
Therefore, in order to use regression for data collected from observations, we need to make it more alike those collected by experiment. Propensity score matching is what transforms data collected from observations to data collected from experiment, by making variables affecting the selection of treatment variable similar among treated and untreated sample.
2015년 8월 25일 화요일
만화로 나누는 오픈소스 이야기: 오픈소스 개발에 참여하는 방법
만화로 나누는 오픈소스 이야기: 오픈소스 개발에 참여하는 방법: 참고 오픈소스 프로젝트에 참여하는 효과적인 방법 [ 다음 ]
2015년 8월 18일 화요일
Binning (=Discretization)
Credit Scoring과 관련된, Binning에 관해 아주 정리가 잘 되어 있는 글.
smbinning package도 R을 배워서 꼭 사용해보도록 해야겠다.
References:
-Revolutionary Analytics.com: http://blog.revolutionanalytics.com/2015/03/r-package-smbinning-optimal-binning-for-scoring-modeling.html
smbinning package도 R을 배워서 꼭 사용해보도록 해야겠다.
References:
-Revolutionary Analytics.com: http://blog.revolutionanalytics.com/2015/03/r-package-smbinning-optimal-binning-for-scoring-modeling.html
2015년 8월 12일 수요일
SVM의 예측모델을 찾아서
머신러닝 알고리즘은 예측 모델(가설)을 만들어내는 알고리즘이다.
SVM이 margin이 최대화되는 hyperplane을 찾는 알고리즘이라는 것은 알고 있지만, 그렇게 hyperplane을 만들고 나서 어떻게 예측을 하는지 궁금해졌다.
더 최초의 동기는 어떤 샘플이 어떤 클래스로 구분되지 못했을 때, 가장 큰 원인이 무엇인지 찾을 수 있는지 알고 싶었다. 즉, ....(editing)
LinearSVC for binary class 에 한하여 SVM의 예측모델 작동방식은 다음과 같다.
- separating hyperplane을 찾는다.
- hyperplane에 orthogonal한 vector를 찾는다.
- 이 vector와 예측하려는 sample과의 dot product를 구한다.
- 이 dot product가 양이면 positive class에 속하고, 음이면 negative class에 속한다.
References:
- CrossValidated: http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/39243/how-does-one-interpret-svm-feature-weights
SVM이 margin이 최대화되는 hyperplane을 찾는 알고리즘이라는 것은 알고 있지만, 그렇게 hyperplane을 만들고 나서 어떻게 예측을 하는지 궁금해졌다.
더 최초의 동기는 어떤 샘플이 어떤 클래스로 구분되지 못했을 때, 가장 큰 원인이 무엇인지 찾을 수 있는지 알고 싶었다. 즉, ....(editing)
LinearSVC for binary class 에 한하여 SVM의 예측모델 작동방식은 다음과 같다.
- separating hyperplane을 찾는다.
- hyperplane에 orthogonal한 vector를 찾는다.
- 이 vector와 예측하려는 sample과의 dot product를 구한다.
- 이 dot product가 양이면 positive class에 속하고, 음이면 negative class에 속한다.
References:
- CrossValidated: http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/39243/how-does-one-interpret-svm-feature-weights
2015년 8월 4일 화요일
Gradient Boosting Machine
Gradient Boosting Machine updates model (= hypothesis) by gradient descent update method.
In gradient descent update for linear regression, logistic regression, or else, betas or parameters in a model are updated through gradient descent.
However in GBM, the model itself is updated through gradient descent, which means that betas or parameters are updated altogether with a single gradient descent.
Useful Resources:
- A Gentle Introduction to Gradient Boosting: http://www.ccs.neu.edu/home/vip/teach/MLcourse/4_boosting/slides/gradient_boosting.pdf
- The Elements of Statistical Learning: http://web.stanford.edu/~hastie/local.ftp/Springer/OLD/ESLII_print4.pdf
2015년 7월 31일 금요일
[editing] Ensemble learning for trees
Problem: Trees can grow too noisy. (= high variance)
Solutions: Bagging, Boosting, Random Forests
General performance: Boosting > Random Forests > Bagging > Single Tree
1. Bagging (= bootstrap aggregation)
- Random samples of equal size -> generate a fitted tree for each
- Average them!
2. Random Forests
- De-correlate! How?
- At each point of split, pick sqrt(number of features) random features as candidates
3. Boosting (= stage-wise additive modeling)
- Adaboost
- Gradient Boosting Machine
References:
2015년 7월 29일 수요일
장인 정신 - 안도 다다오
장인 정신.
본질을 기억하기.
- 관련 링크: http://navercast.naver.com/magazine_contents.nhn?rid=2324&contents_id=95257
2015년 7월 23일 목요일
R project management
References:
- Cross Validated: http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/2910/how-to-efficiently-manage-a-statistical-analysis-project
- Cross Validated: http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/2910/how-to-efficiently-manage-a-statistical-analysis-project
SSE, SEE
SSE(Standard Squared Error): sum((actual y - expected y)^2)
SEE(Standard Error of Estimates): sqrt(SSE/n-k) (where k is the number of variables. e.g. y = 1 + x => k = 2)
SST = SSE + SSR
R^2 = SSR/SST (how accurate regression line is)
SEE(Standard Error of Estimates): sqrt(SSE/n-k) (where k is the number of variables. e.g. y = 1 + x => k = 2)
SST = SSE + SSR
R^2 = SSR/SST (how accurate regression line is)
Tricky, Tricky Credit Scoring System
1. In traditional CSS, it is not multivariate logistic regression, but multiple univariate logistic regressions.
We're running univariate logistic regression for each intervals.
If you visualize it, it looks like a 'line graph' with inflection points(?).
2. What logit in CSS is interested is not expected target value but the slope(=relationship with target = how much score to give per unit increase in the variable).
3. Dummy variables are not used in a way they are used in typical machine learning problems. Don't get fooled.
4.
We're running univariate logistic regression for each intervals.
If you visualize it, it looks like a 'line graph' with inflection points(?).
2. What logit in CSS is interested is not expected target value but the slope(=relationship with target = how much score to give per unit increase in the variable).
3. Dummy variables are not used in a way they are used in typical machine learning problems. Don't get fooled.
4.
2015년 7월 22일 수요일
2015년 7월 17일 금요일
t-test
확률 계산이 아니라 가설 검정을 위해 사용되는 확률 분포
표본의 수가 30개 미만일 때만 사용
References:
- blog: http://math7.tistory.com/55
표본의 수가 30개 미만일 때만 사용
References:
- blog: http://math7.tistory.com/55
p-value
- p-value: probability of supporting null hypothesis
- If p-value < significance, null hypothesis is rejected.
- p-value applies to not only chi-square distribution but also normal distribution
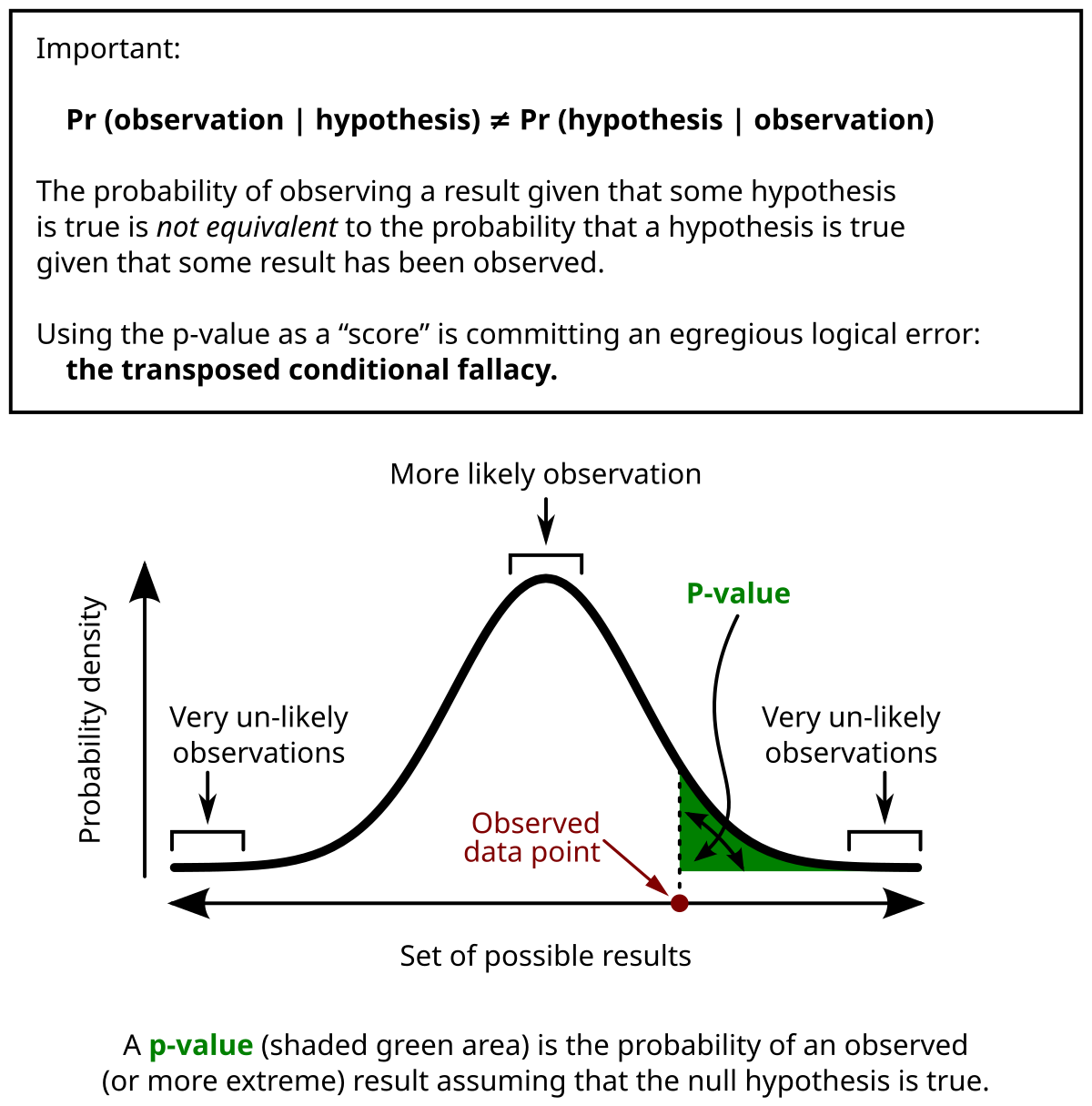
"P-value in statistical significance testing" by User:Repapetilto @ Wikipedia & User:Chen-Pan Liao @ Wikipedia - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:P_value.png. Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Commons.
References:
- blog: http://statistics-cahn.blogspot.kr/2007/10/p-value.html
2015년 7월 16일 목요일
F-score & AUROC
#fscore#fmeasure#f-score#auroc#roc#threshold
I've been using F-scores when validating binary classifiers for imbalanced data set. Recently, I've just found out that using AUROC could make life a bit easier. If I use AUROC, I don't have to find optimal threshold for every new classifiers. The only time I optimize threshold is with the final final classifier.
For a classifier with a given AUROC, there could be many different F-scores as threshold varies.
So,
first, find the classifier with the largest AUROC,
and then, find the threshold that yields the largest F-score.
- Cross Validated: http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/7207/roc-vs-precision-and-recall-curves
I've been using F-scores when validating binary classifiers for imbalanced data set. Recently, I've just found out that using AUROC could make life a bit easier. If I use AUROC, I don't have to find optimal threshold for every new classifiers. The only time I optimize threshold is with the final final classifier.
- F-score: a score for a given threshold
- AUROC: a score for varying threshold
For a classifier with a given AUROC, there could be many different F-scores as threshold varies.
So,
first, find the classifier with the largest AUROC,
and then, find the threshold that yields the largest F-score.
- Cross Validated: http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/7207/roc-vs-precision-and-recall-curves
Dealing with Imbalanced Data Set
1. Use PR(precision-recall) curve instead of AUROC(area under receiver operatic characteristic curve).
- Stack Exchange: http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/64047/effective-validity-of-auroc-as-performance-measure-what-about-very-high-auroc
2. Balance data by down sampling or up sampling
3. Optimize threshold (= cutoff)
4. ...and more to be explored
- Stack Exchange: http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/64047/effective-validity-of-auroc-as-performance-measure-what-about-very-high-auroc
2. Balance data by down sampling or up sampling
3. Optimize threshold (= cutoff)
4. ...and more to be explored
2015년 7월 14일 화요일
Lagrange Multipliers
While studying support section machine...
Lagrangian on optimization problem.
References:
- The Idea Shop: http://www.the-idea-shop.com/article/215/understanding-why-the-method-of-lagrange-multipliers-works
Lagrangian on optimization problem.
References:
- The Idea Shop: http://www.the-idea-shop.com/article/215/understanding-why-the-method-of-lagrange-multipliers-works
2015년 7월 12일 일요일
Discriminative model vs. Generative model
Discriminative model: P(y|x)
- A conditional probability of y given x
- learning h(x) = {0, 1}
- As a rule of thumb, it's faster than generative models.
- Examples: Logistic regression, SVM, Neural networks
Generative model: P(x, y)
- A joint distribution of x and y
- P(x|y) * P(y)
- Possible to induce discriminative model by using Bayes' Theorem
- Possible to generate new data by sampling from P(x, y)
- Examples: Naive Bayes
References:
- Stack Overflow: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/879432/what-is-the-difference-between-a-generative-and-discriminative-algorithm
- Lecture note by Andrew Ng: http://cs229.stanford.edu/notes/cs229-notes2.pdf
- Machine learning lecture by Andrew Ng: http://openclassroom.stanford.edu/MainFolder/VideoPage.php?course=MachineLearning&video=06.1-NaiveBayes-GenerativeLearningAlgorithms&speed=100
- Quora: http://www.quora.com/What-are-the-differences-between-generative-and-discriminative-machine-learning
2015년 7월 1일 수요일
Setting up Monary
#Monary#MongoDB#NumPy#Pandas#PyMongo
I had a hard, hard time setting up data science environment with MongoDB, Monary, Python, Numpy, Pandas.
The problem occurred with Monary! (It converts MongoDB database into NumPy arrays with much faster speed than PyMongo.)
First, install mongo-c-driver.
Then, install monary.
Hughhh, done!!
I had a hard, hard time setting up data science environment with MongoDB, Monary, Python, Numpy, Pandas.
The problem occurred with Monary! (It converts MongoDB database into NumPy arrays with much faster speed than PyMongo.)
First, install mongo-c-driver.
$ brew install git gcc automake autoconf libtool
$ git clone https://github.com/mongodb/mongo-c-driver.git
$ cd mongo-c-driver
$ ./autogen.sh
$ make
$ sudo make install
Then, install monary.
$ hg clone https://bitbucket.org/djcbeach/monary
Hughhh, done!!
2015년 6월 5일 금요일
[사랑의 기술] 에리히 프롬 : 사랑만이 인류를 구할 수 있다
[사랑의 기술] 에리히 프롬
혹시나 이 책을 읽을까 말까 고민하는 사람이라면 꼭. 읽기를 바란다.
초반에 너무 어려워서 그만둘뻔 했는데, 고비를 넘기니 보물이 있었다.
다른 사람에게는 뒤에 제자 라이너 풍크의 글부터 읽고 시작하기를 권하고 싶다. 에리히 프롬이 어떤 사람인지 어떤 삶을 살았는지 왜 이 책을 썼는지 알고나면 좀 더 잘 읽힐 것 같다.
이 책이 나에게 던진 메세지는
'사랑만이 인류를 구할 수 있다'
였다.
학창시절 어디선가 들어본 '에리히 프롬'이라는 이름. 그가 얼마나 당시 인류가 처한 위기를 깊이 느끼고, 이를 해결하기 위해 연구와 일상을 통해 노력하고 실천하였는지 읽는 것은 내게 감동이었다. 특히나 제자 라이너 풍크가 묘사한 에리히 프롬의 따뜻하고도 강렬한 시선은 내가 너무나도 갖고 싶은 시선이다.
(나중에 좀 더 생각을 덧붙일 예정이다.)
혹시나 이 책을 읽을까 말까 고민하는 사람이라면 꼭. 읽기를 바란다.
초반에 너무 어려워서 그만둘뻔 했는데, 고비를 넘기니 보물이 있었다.
다른 사람에게는 뒤에 제자 라이너 풍크의 글부터 읽고 시작하기를 권하고 싶다. 에리히 프롬이 어떤 사람인지 어떤 삶을 살았는지 왜 이 책을 썼는지 알고나면 좀 더 잘 읽힐 것 같다.
이 책이 나에게 던진 메세지는
'사랑만이 인류를 구할 수 있다'
였다.
학창시절 어디선가 들어본 '에리히 프롬'이라는 이름. 그가 얼마나 당시 인류가 처한 위기를 깊이 느끼고, 이를 해결하기 위해 연구와 일상을 통해 노력하고 실천하였는지 읽는 것은 내게 감동이었다. 특히나 제자 라이너 풍크가 묘사한 에리히 프롬의 따뜻하고도 강렬한 시선은 내가 너무나도 갖고 싶은 시선이다.
(나중에 좀 더 생각을 덧붙일 예정이다.)
2015년 4월 9일 목요일
creative thinking - logical thinking - understanding
creative thinking
logical thinking
understanding
아주 아주 클리셰. 지식의 단순 이해보다는 그 지식을 가지고 논리적으로, 창의적으로 생각하는 것이 훨씬 중요하다는 말.
하지만 아주 아주 실천하기 어려운 일. 자꾸 더 많은 지식을 집어 넣으려고만 한다. 중요한 건 그게 아닌데. 지식을 갖고 노는 능력이 훨 중요한데.
항상 중요한 게 무엇인지 까먹지 말자!
그걸 알아봐주는 사람은
있.다.
logical thinking
understanding
아주 아주 클리셰. 지식의 단순 이해보다는 그 지식을 가지고 논리적으로, 창의적으로 생각하는 것이 훨씬 중요하다는 말.
하지만 아주 아주 실천하기 어려운 일. 자꾸 더 많은 지식을 집어 넣으려고만 한다. 중요한 건 그게 아닌데. 지식을 갖고 노는 능력이 훨 중요한데.
항상 중요한 게 무엇인지 까먹지 말자!
그걸 알아봐주는 사람은
있.다.
자신의 약한 모습을 드러낼 수 있는 사람이 진짜 강한 사람이다.
자신의 약한 모습을 드러낼 수 있는 사람이 진짜 강한 사람이다.
어제의 깨달음
그리고
어제의 실천
나의 가장 소중한 사람들에게 내 약한 모습을 드러내 버렸다. 드러냈다?
그게 어떻게 보면 1년이 걸렸고, 또 어떻게 보면 25년이 걸렸다.
나는 완벽하지 않은 상태에 대한 일종의 공포를 가진 사람이다. (이걸 Atelophobia (fear of imperfection)이라고 하더라. 관련 글을 몇 개 읽어봤는데 구구절절 내 얘기 같다.) 지금은 그래도 많이 극복이 되었지만 발표의 순간이 오면 얼굴이 새빨게지곤 했다. 조금이라도 실수할까봐 남들이 이상하게 보면 어떡하지 걱정하는 게 몸에 뱄다. 내 생각을 이야기하는 게 두려웠다. 이상하게 생각할까봐.
그리고 이런 성향은 내가 경쟁적인 한국의 입시제도의 첨단을 달리면서 더욱 강해졌다. 아무리 잘해도 그것은 칭찬거리가 되지 못했다. 오히려 나는 조금의 부족한 부분을 확대경을 끼고 보아 그 부분을 메꾸어야 했다. 그래서 나는 인생에서 거의 성취감을 느껴본 적이 없다. 이런 말을 들으면 사람들은 많이 놀랄 것이다. 성취라면 성취라고 할 수있는 크고 작은 일들이 있었지만, 나는 그 안에서 항상 나의 부족함을 보았다. 그걸 겸손이라고 생각했다. 하지만 그건 겸손이라기보다는 자기 비하에 가까운 것이 아니었을까. 부족한 상태의 나를 사랑하지 못했다. 부족은 나에게 곧 스트레스를 의미했다. 부족한 것의 발견은 자동적으로 내게 스트레스를 준다. 그리고 이러한 스트레스는 내가 괴로운 고3시절을 보내게 된 가장 큰 이유다.
대학 입학 이후 갈 길을 몰라 방황했던 이유도. 내 생각에 자신이 없었으니까. 어떤 길을 가려고 해도 그 길의 여행을 이끌고 나갈 힘이 내겐 없었다. 도대체 그것이 무엇이길래. 그 힘은 공부를 잘하는 것과는 아주 아주 별개의 문제였다.
어제는 이 모든 두려움을 이기고 나의 가장 큰 약점을 드러냈다.
'나는 부족한 나를 사랑할 자존감이 부족하다는 것.'
개인적으로 너무나 큰 일을 해낸 나를 정말 응원해주고 싶다.
이젠 조금씩 그 자존감을 채워나갈 일만 남았다.
부족한 부분에 한숨짓기 보다는
조금씩 쌓아가는 내 모습을 사랑해야지.
어제의 깨달음
그리고
어제의 실천
나의 가장 소중한 사람들에게 내 약한 모습을 드러내 버렸다. 드러냈다?
그게 어떻게 보면 1년이 걸렸고, 또 어떻게 보면 25년이 걸렸다.
나는 완벽하지 않은 상태에 대한 일종의 공포를 가진 사람이다. (이걸 Atelophobia (fear of imperfection)이라고 하더라. 관련 글을 몇 개 읽어봤는데 구구절절 내 얘기 같다.) 지금은 그래도 많이 극복이 되었지만 발표의 순간이 오면 얼굴이 새빨게지곤 했다. 조금이라도 실수할까봐 남들이 이상하게 보면 어떡하지 걱정하는 게 몸에 뱄다. 내 생각을 이야기하는 게 두려웠다. 이상하게 생각할까봐.
그리고 이런 성향은 내가 경쟁적인 한국의 입시제도의 첨단을 달리면서 더욱 강해졌다. 아무리 잘해도 그것은 칭찬거리가 되지 못했다. 오히려 나는 조금의 부족한 부분을 확대경을 끼고 보아 그 부분을 메꾸어야 했다. 그래서 나는 인생에서 거의 성취감을 느껴본 적이 없다. 이런 말을 들으면 사람들은 많이 놀랄 것이다. 성취라면 성취라고 할 수있는 크고 작은 일들이 있었지만, 나는 그 안에서 항상 나의 부족함을 보았다. 그걸 겸손이라고 생각했다. 하지만 그건 겸손이라기보다는 자기 비하에 가까운 것이 아니었을까. 부족한 상태의 나를 사랑하지 못했다. 부족은 나에게 곧 스트레스를 의미했다. 부족한 것의 발견은 자동적으로 내게 스트레스를 준다. 그리고 이러한 스트레스는 내가 괴로운 고3시절을 보내게 된 가장 큰 이유다.
대학 입학 이후 갈 길을 몰라 방황했던 이유도. 내 생각에 자신이 없었으니까. 어떤 길을 가려고 해도 그 길의 여행을 이끌고 나갈 힘이 내겐 없었다. 도대체 그것이 무엇이길래. 그 힘은 공부를 잘하는 것과는 아주 아주 별개의 문제였다.
어제는 이 모든 두려움을 이기고 나의 가장 큰 약점을 드러냈다.
'나는 부족한 나를 사랑할 자존감이 부족하다는 것.'
개인적으로 너무나 큰 일을 해낸 나를 정말 응원해주고 싶다.
이젠 조금씩 그 자존감을 채워나갈 일만 남았다.
부족한 부분에 한숨짓기 보다는
조금씩 쌓아가는 내 모습을 사랑해야지.
2015년 4월 3일 금요일
machine learning recap - until supervised learning
학교 Data Science 수업과 Coursera에서 제공하는 Machine Learning by Andrew Ng을 동시에 수강중이다. 학교 수업은 사실상 Andrew Ng 수업의 강의 자료를 바탕으로 수업중!
처음엔 수월했는데 한 달 쯤 지나니 머리가 살짝 아파오기 시작한다.
정리가 필요해!
2. 어떤 모델을 만들지 구상했다면, 모델을 실제로 만들어야지!
처음엔 수월했는데 한 달 쯤 지나니 머리가 살짝 아파오기 시작한다.
정리가 필요해!
Machine Learning
- Supervised Learning: knows target variable
- Unsupervised Learning: don't know (usually involves clustering data)
Supervised Learning Algorithm: 한 마디로 '예측 모델(hypothesis)'을 만드는 알고리즘
1. 모델 모양 정하기:
linear regression, polynomial regression(quadratic regression, cubic regression, etc), logarithmic regression, logistic regression 등 등 여러가지 모델 중에서 데이터 성격에 맞는 것으로다가 택일!
target variable이 continuous하고 포물선으로 분포한다 -> quadratic regression
target variable이 discrete하다 -> logistic regression (계단 모양이라 discrete value를 설명하기에 적합)
2. 어떤 모델을 만들지 구상했다면, 모델을 실제로 만들어야지!
- Gradient Descent으로 만들기: 모델에 들어갈 파라미터를 임의로 하나 선정하고 조금씩 그 파라미터를 수정하여 마침내 최적의 파라미터를 찾아내는 방법 (feature가 많아지면 유리함)
- Normal Function으로 만들기: 매트릭스로 한방에 구하는 방법 (feature가 많아지면 시간이 오래 걸림)
모델 만들 때, training data에 overfitting되는 문제(training data를 완벽하게 설명하지만 너무 복잡해져서 new data를 제대로 예측하지 못하게 되는 문제)를 피하기 위해서 regularization 필요! -> 각 feature의 영향력을 축소하라! -> how? cost function에 lambda * parameter 값을 추가! (*요 부분은 직관적인 이해를 위해 좀 더 공부가 필요! right now! 쫌 있다 강의 듣고 정리할거임)
3. 이제 모델이 완성되었다. 새로운 데이터를 모델에 넣고 target variable을 예측해보자!
머신러닝이란 대략 이러한 것이다. (것인 것 같다...)
지금까지는 그냥 통계인 것 같다. (비록 통계를 제대로 배워본 적은 없지만, 지금까지의 내용은 inferential statistics 의 범주에 들어가지 않나 싶다 *정확하지 않음)
지금까지는 그냥 통계인 것 같다. (비록 통계를 제대로 배워본 적은 없지만, 지금까지의 내용은 inferential statistics 의 범주에 들어가지 않나 싶다 *정확하지 않음)
2015년 3월 22일 일요일
가장 따뜻한 색 블루
이 영화의 아름다움은 아주 선정적이고 자극적일 수 있는 소재를
오히려 아주 일상적이고 담담하게 다루었다는 데 있다.
그냥 수많은 사랑 이야기 중 하나로 느껴졌다.
그래서 나는 여자와 여자의 사랑이라는 어색하고 불편한 소재 안에서
그들의 사랑을 발견할 수 있었다.
그리고 그들의 이별도.
한 마디로 가장 따뜻한 색 블루는 그냥 평범한 사랑이야기였다.
그리고 이건 이 영화에 대한 찬사다.
- The End -
지식의 쓰임
가장 가치 있는 지식의 쓰임은
새로운 지식을 만들어내는 것이다.
단지 알기 위해서 지식을 배워왔으나
그것은 아무 것도 아니다.
힘겹게 지식을 만들어내야 한다.
아주 허술한 것이라 할 지라도 계속 만들어내야 한다.
그것이 사람을 사람답게 하는 것이다.
#가장 따뜻한 색 블루
2015년 3월 19일 목요일
Gradient descent
Gradient descent (in 3D matrix) in a nutshell:
How:
What it means:
From a random point in 3D, finding a bottom or bottoms, by gradually moving downward.
How:
repeat {
θj := θj − α (∂J(θ)/∂θj)
} (simultaneously update for j = 0 and j = 1)
What it means:
If current standpoint is on / this shape of slope, go left and if \, go right.
This is just common sense. Assume you are climbing down the mountain. It the slope is / shape, you go left, and go right otherwise. As simple as that.
2015년 3월 17일 화요일
(나는) 알고리즘을 왜 배우는가
사실 내가 알고리즘 강의를 듣기 시작한 이유는 데이터 사이언스 강의의 선수과목이기 때문이다.
그 외에는 이유가 없었다.
알고리즘이 뭔지도 고민해보지 않고 시작한 강의.
1강을 겨우 마무리한 이 시점에 왜 알고리즘을 배워야하는지 정리해 볼 필요가 있다.
내 생각에 알고리즘을 배워야 하는 이유는 노가다가 아닌 우아한 방법으로 빠르고 가벼운 프로그램을 만들기 위해서다.
많은 문제들은 노가다로 해결 가능한 경우가 많다. 고등학교 수학 문제들만 해도 그렇다.
'아,, 이거 노가다하면 풀긴 풀 수 있는데, 시험 시간이 모자라는데,,,ㅠㅠ'
다들 이런 생각 한 번쯤 해보지 않았는가.
그런데, 완전 우아하게 문제를 풀 수 있는 방법이 생각날 때가 있다.
'와우! 엄청 빨리 풀렸어! 이제 다른 문제 좀 살펴봐야겠어!!'
자원을 아끼면 다른 더 중요한 곳에 자원을 쓸 수 있다.
그래서 내가 알고리즘을 배우는 이유는 가볍고 우아한 프로그램을 만들기 위해서다.
해결책이 간단할수록 오류도 적게 나지 않는가.
알고리즘. 그것은 우아한 프로그램을 위한 날개.
2015년 3월 16일 월요일
열정과 일중독
오늘의 대화 주제 중에 하나. 열정과 일중독.
친구(친): 열정적인 것과 일중독은 다르다는 친구의 말.
나: 열정적인 거랑 일중독이랑 뭐가 달라?
친: 음, 뭐라고 설명하긴 힘든데, 두 방향은 아주 다른 결과를 낳는다고 생각해.
--- 여러가지 이야기 ---
나: 아, 이제 알겠어!
열정적인 것은 하고 싶어서 하는 거고, 일중독은 하지 않는 것을 참을 수 없어서 하는 거야.
나 같다. 뭔가 하지 않으면 불안해서 참지 못해, 대학 시절 방학에 뭔가 해야만 한다는 강박에 사로잡혔던 것. (지금도 대학 시절 중이긴 합니다만)
하고 싶은 것을 열심히 하는 것은 참된 기쁨을 주지만
무언가 하지 않으면 불안해서 열심히 하는 것은 공허함을 줄 뿐이다.
인생을 참된 기쁨으로 채워야겠다.
- 오늘의 일기 끝
친구(친): 열정적인 것과 일중독은 다르다는 친구의 말.
나: 열정적인 거랑 일중독이랑 뭐가 달라?
친: 음, 뭐라고 설명하긴 힘든데, 두 방향은 아주 다른 결과를 낳는다고 생각해.
--- 여러가지 이야기 ---
나: 아, 이제 알겠어!
열정적인 것은 하고 싶어서 하는 거고, 일중독은 하지 않는 것을 참을 수 없어서 하는 거야.
나 같다. 뭔가 하지 않으면 불안해서 참지 못해, 대학 시절 방학에 뭔가 해야만 한다는 강박에 사로잡혔던 것. (지금도 대학 시절 중이긴 합니다만)
하고 싶은 것을 열심히 하는 것은 참된 기쁨을 주지만
무언가 하지 않으면 불안해서 열심히 하는 것은 공허함을 줄 뿐이다.
인생을 참된 기쁨으로 채워야겠다.
- 오늘의 일기 끝
2015년 3월 14일 토요일
typedef in C
typedef struct node
{
void* dataPtr;
struct node* link;
} NODE;Q1: why use 'node' when 'NODE' is the name?
-> node is part of an old type name, 'struct node'. It is not a new type name.
- this is the typedef syntax: typdef oldTypeName newTypeName
- struct node{ ... } = OldTypeName
- NODE = NewTypeName
- it's possible to define NODE without node!
typedef struct
{
void* dataPtr;
struct* link;
} NODE;Pointer to void in C
void* p (or void *p) :
- p: variable(name)
- *p: implies p is a pointer
- void: to what data type the pointer points to (since the data type is void, no need to assign any value to void)
- void *p: pointer to void (pointer's name is p)
int i = 7;
- i: variable
- int: i's data type
- 7: i's value
- int i = 7: integer i has a value of 7
p = &i:
- assign to p the address of i
2015년 2월 3일 화요일
python mini glossary [editing]
primitive constructs
1) objects
scalar/unstructured: int, float, bool, None
non-scalar/structured: str, tuple, list, dict
function
2) operators: type specific
expression: when entered, it has a value (it returns an object)
argument: parameter
1) objects
scalar/unstructured: int, float, bool, None
non-scalar/structured: str, tuple, list, dict
function
2) operators: type specific
expression: when entered, it has a value (it returns an object)
argument: parameter
Descriptive Statistics & Inferential Statistics
Descriptive Statistics: '그렇다'라고 말하는 것. (To say 'it is'.)
Inferential Statistics: '그럴 것이다'라고 말하는 것. (To say 'it is expected to be.')
+Descriptive, Predictive, Forecasting(Prescriptive)
Inferential Statistics: '그럴 것이다'라고 말하는 것. (To say 'it is expected to be.')
+Descriptive, Predictive, Forecasting(Prescriptive)
2015년 1월 28일 수요일
Software & Hardware
What distinguishes software from hardware is the fact that it's alive.
It changes over time unlike hardware that don't.
Then, what makes software alive? ( = easy to change?)
* small thought: These days, however, hardware is becoming alive(= easier to change) with modularization. See Google's Ara. Software's 'softness' is being injected into hardware.
It changes over time unlike hardware that don't.
Then, what makes software alive? ( = easy to change?)
- Modularity (makes codes easy to fix)
- Careful documentation of specification (makes codes readable)
- Defensive programming (makes bugs easier to detect)
* small thought: These days, however, hardware is becoming alive(= easier to change) with modularization. See Google's Ara. Software's 'softness' is being injected into hardware.
2015년 1월 15일 목요일
Algorithms - baby step
1. Straight line algorithms: every code is executed, no reuse (construct: sequence)
2. Branching algorithms: some codes are not executed, no reuse (construct: selection)
3. Iterative algorithms (looping algorithms): reuse code (construct: loop)
-> ways to generate guesses:
1) Exhaustive enumeration
2) Bisection search: faster
3) Newton-Raphson method: even faster
4. Recursive algorithms: call code multiple times (same code within the code, fractal)
2. Branching algorithms: some codes are not executed, no reuse (construct: selection)
1] conditional statement (if, elif, else)
3. Iterative algorithms (looping algorithms): reuse code (construct: loop)
1] guess and check algorithms (for, while loop)
-> ways to generate guesses:
1) Exhaustive enumeration
2) Bisection search: faster
3) Newton-Raphson method: even faster
4. Recursive algorithms: call code multiple times (same code within the code, fractal)
2015년 1월 14일 수요일
Functions
Functions: Custom-made functions cf) built-in functions
Expressions: Everything that returns value. cf) statements
Control:
Invocation: invoke = call
- Make your own functions and play with it like Lego block.
- Clients don't have to know what's inside the block. If the block is what you want, you can use it without knowing how it is structured inside.
- Functions are composed of primitive calculations and algorithms. However, from a broad view, functions become primitive calculations that belong to broader algorithms.
Expressions: Everything that returns value. cf) statements
source: https://docs.python.org/2/glossary.html
Control:
Invocation: invoke = call
피드 구독하기:
덧글 (Atom)